testing phenomenon easy to hard|hard and easy problems : trading Moravec's paradox is the observation in artificial intelligence and robotics that, contrary to traditional assumptions, reasoning requires very little computation, but sensorimotor and perception skills require enormous computational resources. The principle was articulated by Hans Moravec, Rodney Brooks, Marvin Minsky and others in the 1980s. Moravec wrote in 1988: "it is comparatively easy to make computers exhibit adult level performance on intelligence tests or playing checker. WEB3 dias atrás · Ladbrokes UK Open 2024 Darts. 📝 Format: 160-player knockout draw (higher seed join later), From best-of-11 to best-of-21 in the Final. 🏟️ Venue: Butlins Resort Minehead, Somerset, England. 🗓️ Dates: Friday, 1 March to Sunday, 3 March 2024.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 11 de dez. de 2023 · Gols e melhores momentos Brighton 2x0 Ajax pela Europa League | 11/12/2023 - VAVEL Brasil. 2 - 0. 1-0, min. 43, João .
testing phenomenon explained
In this paper, I evaluate three demarcation criteria for dividing phenomena into hard and easy problems: functional definability, the puzzle of the accompanying phenomenon, and the first-person data of subjective experience.Moravec's paradox is the observation in artificial intelligence and robotics that, contrary to traditional assumptions, reasoning requires very little computation, but sensorimotor and perception skills require enormous computational resources. The principle was articulated by Hans Moravec, Rodney Brooks, Marvin Minsky and others in the 1980s. Moravec wrote in 1988: "it is comparatively easy to make computers exhibit adult level performance on intelligence tests or playing checker. The testing effect is a finding from cognitive psychology with relevance for education. It shows that after an initial study period, taking a practice test improves long-term .
The "testing" phenomenon refers to the finding that students who take a test on material between the time they first study and the time they take a final test remember more of the .
In this paper, I evaluate three demarcation criteria for dividing phenomena into hard and easy problems: functional definability, the puzzle of the accompanying phenomenon, and the first .
This phenomenon has been referred to as the easy-to-hard effect. It occurs in several modalities and species (for review, see Wisniewski, Radell, Church, & Mercado, 2017 ). One account of .Due to the fundamental limitation of the empirical method, no permanent scientific truth (or its absence) can be established by empirical replications. Phenomenon replications, however, . Solving it requires explaining why the relationship between brain and experience is the way it is and not some other way. We use the tools of the interventionist theory of .
This paper provides an overview of resonating structures in the fields of neuroscience, biology and physics and offers a possible solution to what we see as the “easy .
The phenomenon of consciousness, thus, is incorporating aspects of both an empirically testable trait and a concept not subject to empirical study, and I suggest to . People tend to gravitate towards what they find easy to process, leading to a greater inclination towards familiar options. Classical Conditioning Classical conditioning mechanisms underlie aspects of the mere exposure .
In the philosophy of mind, the hard problem of consciousness is to explain why and how humans and other organisms have qualia, phenomenal consciousness, or subjective experience. [1] [2] It is contrasted with the "easy problems" of explaining why and how physical systems give a (healthy) human being the ability to discriminate, to integrate information, and to perform .Moravec's paradox is the observation in the fields of artificial intelligence and robotics that, contrary to traditional assumptions, reasoning requires very little computation, but sensorimotor and perception skills require enormous computational resources. The principle was articulated in the 1980s by Hans Moravec, Rodney Brooks, Marvin Minsky, and others. The “Easy Part” of the Hard Problem. The “easy part” of the Hard Problem is, as discussed above, more generally known as the “combination problem” or the “binding problem” (Chalmers, 2017). The combination problem refers to the question of how different micro-entities combine to form a higher-level macro-conscious entity. David Chalmers has distinguished the “hard” and the “easy” problem of consciousness, arguing that progress on the “easy problem”—on pinpointing the physical/neural correlates of consciousness—will not necessarily involve progress on the hard problem—on explaining why consciousness, in the first place, emerges from physical processing. Chalmers, .
Why Our Minds Swap Out Hard Questions For Easy Ones “When faced with a difficult question, we often answer an easier one instead, usually without noticing the substitution,” writes psychologist and Nobel Prize winner Daniel Kahneman, in a new book. . Straus and Giroux, 2011), which includes a passage on the wheel of fortune test. The Presidential Fitness test, a national physical fitness testing program conducted in United States public middle and high schools from the late 1950s until 2013, contained six various exercises: curl-up, push-up, the sit-and-reach, the 30-foot "shuttle run," the one-mile endurance run, and what sixth discipline testing your biceps and lats?
testing phenomenon experiments
In contrast, phenomenon replications test phenomena in varied forms, contexts, . The upshot is that the establishment of scientific truth is as hard, if not harder, in psychological as in other sciences. . (Bavel et al., 2016) makes it relatively easy to conduct, unwittingly or not, replication experiments to produce refuting evidence. One .Hard–easy effect, the tendency to overestimate one's ability to accomplish hard tasks, and underestimate one's ability to accomplish easy tasks. [ 5 ] [ 80 ] [ 81 ] [ 82 ] Illusion of explanatory depth , the tendency to believe that one understands a topic much better than one actually does.Impact hammer testing has many advantages, including broad adaptability and easy implementation. For instance, with even only one accelerometer on hand, we can obtain all FRFs by roving the impacted locations and utilizing the reciprocal theorem. During an impact hammer testing, there are two crucial problems to be addressed. The first is to In this context of software testing, test as a noun refers to a test case: a single, independent, addressable scenario, such as the "relationship between sequences" test case in the previous example. Individually named tests are useful for the following tasks, among others: Determining how a test succeeds or fails over time.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables, make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Regular blood sugar testing: Frequent testing can help identify blood sugar patterns and can assist in differentiating between the Somogyi effect and dawn phenomenon. Testing might be required in the middle of the night (around 2 a.m to 3 a.m) when hypoglycemia is suspected. If all goes to plan, the 55-foot-long Phenomenon catamaran powered by four 3,000-hp turbine engines should be testing on Sarasota Bay (Fla.) in the next couple of hours according to Scott Barnhart, the throttleman for the cat. The boat will attempt to break the propeller-driven water-speed record of 220 mph tomorrow during the Super Boat International Kilo Runs on the .The hard–easy effect is a cognitive bias that manifests itself as a tendency to overestimate the probability of one's success at a task perceived as hard, and to underestimate the likelihood of one's success at a task perceived as easy. The hard-easy effect takes place, for example, when individuals exhibit a degree of underconfidence in answering relatively easy questions and a . The Tullio phenomenon is a symptom or physical exam finding, whereas nystagmus or vertigo are induced in response to sound. Professor Pietro Tullio in Bologna, Italy, described this in animals nearly 90 years ago. In humans, the phenomenon was first observed in patients suffering from advanced syphilis. Since then, numerous reports and studies have .
Both laws and theories depend on basic elements of the scientific method, such as generating a hypothesis, testing that premise, finding (or not finding) empirical evidence and coming up with conclusions.Eventually, other scientists must be . Now instead of testing \(1000\) plant extracts, imagine that you are testing just one. If you are testing it to see if it kills beetle larvae, you know (based on everything you know about plant and beetle biology) there's a pretty good chance it will work, so you can be pretty sure that a \(P\) value less than \(0.05\) is a true positive.
select Your test 30 Seconds Test 1 Minute Test 2 Minutes Test 3 Minutes Test 5 Minutes Test 10 Minutes Test Easy Text Medium Text Hard Text Benchmark (2 min) Certificate Tricky Spelling Blind Typing Story Typing. What is phenomenology? Phenomenology in qualitative research is characterized by a focus on understanding the meaning of lived experience from the perspective of the individual.. Instead of testing hypotheses or seeking to generalize findings to a larger population, phenomenological research aims to illuminate the specific and to challenge structural or . History of Standardized Testing. Standardized tests have been a part of American education since the mid-1800s. Their use skyrocketed after 2002’s No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB) mandated annual testing in all 50 states. However, failures in the education system have been blamed on rising poverty levels, teacher quality, tenure policies, and, increasingly, on the .
L'effet de la multiplicite des tests intermediaires sur la memorisation est repris a travers quatre experiences qui tentent de determiner les facteurs d'accroissement des scores qui en decoulent selon les divers modes de rappel (rappel libre, phrases a completer, reconnaissance), et selon les intervalles entre epreuves
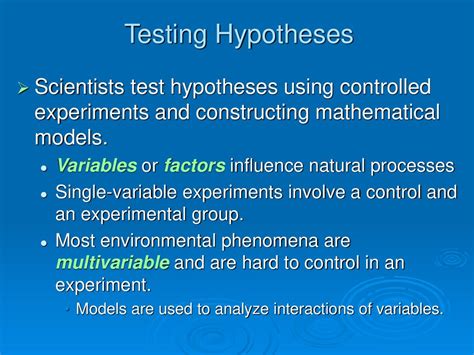
Hypothesis testing example. You want to test whether there is a relationship between gender and height. Based on your knowledge of human physiology, you formulate a hypothesis that men are, on average, taller than women. To test this hypothesis, you restate it as: H 0: Men are, on average, not taller than women. H a: Men are, on average, taller .
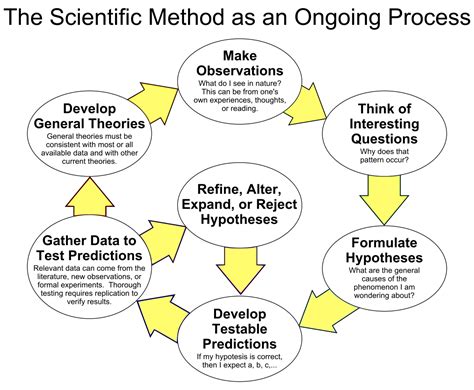
Sputum test. A sample of fluid from your lungs (sputum) is taken after a deep cough and analyzed to help pinpoint the cause of the infection. Your doctor might order additional tests if you're older than age 65, are in the hospital, or have serious symptoms or health conditions. These may include: CT scan.Practice Typing Test. Select difficulty level . About; Features; Tour; Knowledge Base; Blog; Help; Terms of ServiceThe scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century. The scientific method involves careful observation coupled with rigorous scepticism, because cognitive assumptions can distort the interpretation of the observation.Scientific inquiry includes creating a hypothesis through .
web2 dias atrás · Special note about impostors. This site, fitgirl-repacks.site is THE ONLY official site of my repacks. Every single FG repack installer has a link inside, which leads here. ALL other “mirrors” (fitgirlrepacks.co, fitgirl-repacks.cc, fitgirl-repack.com, etc.) are fakes, made to infect you with malware, show you tons of ads and get your money as donations.
testing phenomenon easy to hard|hard and easy problems